

|
latest version v1.9 - last update 10 Apr 2010 |
|
Vector container class. More...
#include <ltiVector.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| vector () | |
| vector (const int &theSize, const T &iniValue=T()) | |
| vector (const int &theSize, const T data[]) | |
| vector (const int &theSize, T data[], const bool constRef) | |
| vector (const vector< T > &other) | |
| vector (const genericVector< T > &other) | |
| vector (const vector< T > &other, const int &from, const int &to=MaxInt32) | |
| vector (const vector< T > &other, const genericVector< int > &idx) | |
| vector (const std::vector< T > &other) | |
| vector (const bool &init, const int &theSize) | |
| virtual | ~vector () |
| const char * | getTypeName () const |
| virtual mathObject * | clone () const |
| bool | prettyCloseTo (const vector< T > &other, const T &tolerance) const |
Arithmetical Operations | |
| T | dot (const vector< T > &other) const |
| vector< T > & | emultiply (const vector< T > &other) |
| vector< T > & | emultiply (const vector< T > &first, const vector< T > &second) |
| vector< T > & | edivide (const vector< T > &other) |
| vector< T > & | edivide (const vector< T > &first, const vector< T > &second) |
| vector< T > & | edivide (const T cst) |
| vector< T > & | edivide (const vector< T > &other, const T cst) |
| vector< T > & | add (const vector< T > &other) |
| vector< T > & | add (const vector< T > &first, const vector< T > &second) |
| vector< T > & | add (const T cst) |
| vector< T > & | add (const vector< T > &other, const T cst) |
| vector< T > & | operator+= (const T cst) |
| vector< T > & | operator+= (const vector< T > &other) |
| vector< T > & | addScaled (const T b, const vector< T > &other) |
| vector< T > & | addScaled (const T a, const vector< T > &first, const T b, const vector< T > &second) |
| vector< T > & | addScaled (const vector< T > &first, const T b, const vector< T > &second) |
| vector< T > & | subtract (const T cst) |
| vector< T > & | subtract (const vector< T > &other, const T cst) |
| vector< T > & | subtract (const vector< T > &other) |
| vector< T > & | subtract (const vector< T > &first, const vector< T > &second) |
| vector< T > & | operator-= (const vector< T > &other) |
| vector< T > & | operator-= (const T cst) |
| vector< T > & | multiply (const T cst) |
| vector< T > & | multiply (const vector< T > &other, const T cst) |
| vector< T > & | operator*= (const T cst) |
| vector< T > & | divide (const T cst) |
| vector< T > & | divide (const vector< T > &other, const T cst) |
| vector< T > & | operator/= (const T cst) |
| T | sumOfElements () const |
| T | productOfElements () const |
find extreme values | |
| T | minimum () const |
| int | getIndexOfMinimum () const |
| T | maximum () const |
| int | getIndexOfMaximum () const |
| void | getExtremes (T &theMinimum, T &theMaximum) const |
| void | getIndexOfExtremes (int &theIdxMinimum, int &theIdxMaximum) const |
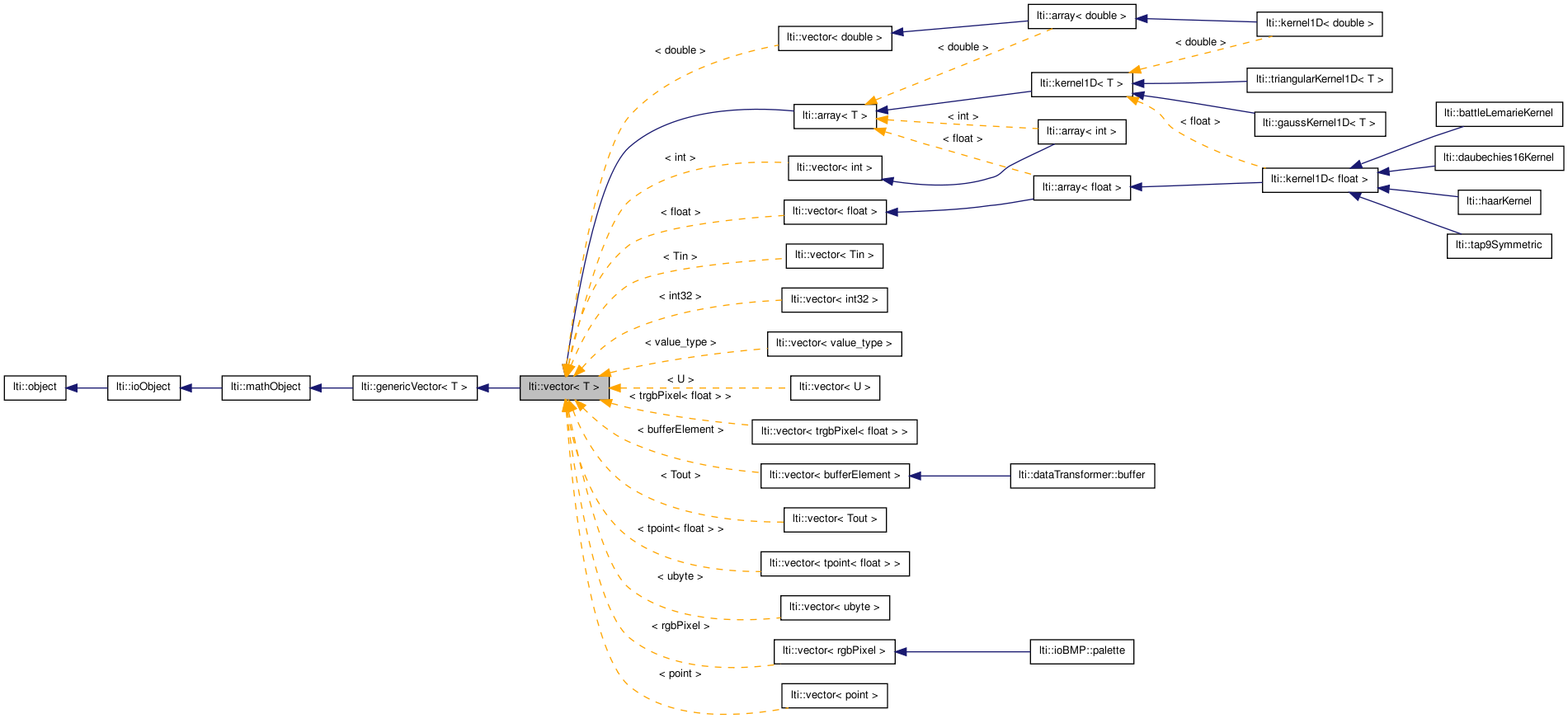
Vector container class.
The lti::vector class allows the representation of n-dimensional vectors. The elements of the vector will be indexed between 0 an n-1.
Note that this class is NOT intended to be a subtitute for std::vector. If you need a vector of elements which use some sort of dynamic memory allocation then you should use the std::vector class of the Standard Template Library.
Only following types are supported by lti::vector:
If you need the vector as container of any other type, consider using the std::vector or the lti::genericVector.
The vector class is a container class implemented as template, but it is by no means a generic container, since the types it supports must fulfill many requirenments, specially support for all arithmetical operators.
If you need to create a vector of floats with 256 elements all initialized with a value of 4.27 just create it:
lti::vector<float> myVct(256,4.27f) // creates vector with 256 elements // all initialized with 4.27f
To access the vector elements use the access operators at() (or the overloaded operator[]()). For example:
float accu = 0; // initialize accumulator for (int i = 0; i < myVct.size(); i++) { tmp += myVct.at(i); // access each element of the vector }
The vector has following methods:
| lti::vector< T >::vector | ( | ) |
default constructor creates an empty vector;
| lti::vector< T >::vector | ( | const int & | theSize, | |
| const T & | iniValue = T() | |||
| ) | [explicit] |
| lti::vector< T >::vector | ( | const int & | theSize, | |
| const T | data[] | |||
| ) |
create a vector of the given size and initialize it with the given data.
The data will be copied.
| theSize | number of elements of the vector. | |
| data | a pointer to the data that will be copied. |
| lti::vector< T >::vector | ( | const int & | theSize, | |
| T | data[], | |||
| const bool | constRef | |||
| ) |
create a vector of the given size and initialize it with the given data, the same way "useExternData" does.
The data will not be copied!.
| theSize | number of elements of the vector. | |
| data | a pointer to the data that will be used. | |
| constRef | if this parameter is true, it will not be possible to change the pointer to the external memory block nor to resize the vector. Despite this, the value of each element can be changed by the access operators. For Example: |
| lti::vector< T >::vector | ( | const vector< T > & | other | ) |
| lti::vector< T >::vector | ( | const genericVector< T > & | other | ) |
create this vector as a copy of another genericVector
| other | the vector to be copied. |
| lti::vector< T >::vector | ( | const vector< T > & | other, | |
| const int & | from, | |||
| const int & | to = MaxInt32 | |||
| ) |
| lti::vector< T >::vector | ( | const vector< T > & | other, | |
| const genericVector< int > & | idx | |||
| ) |
| lti::vector< T >::vector | ( | const std::vector< T > & | other | ) |
| lti::vector< T >::vector | ( | const bool & | init, | |
| const int & | theSize | |||
| ) |
If init is true this constructor is equivalent to calling vector(const int& theSize), and thus initializing all elements with T().
However, in some cases the elements need not be initialized during construction, since complex initializion is required. Especially for large vectors, the unnecessary constructor initialization is very time consuming.
If init is false, memory is allocated but no initialization takes place. Thus the following is equivalent:
vector<int> a(false,10000); matrix<int> a; a.resize(10000,0,false,false);
| virtual lti::vector< T >::~vector | ( | ) | [virtual] |
destructor
| vector<T>& lti::vector< T >::add | ( | const vector< T > & | other, | |
| const T | cst | |||
| ) |
| vector<T>& lti::vector< T >::add | ( | const T | cst | ) |
| vector<T>& lti::vector< T >::add | ( | const vector< T > & | first, | |
| const vector< T > & | second | |||
| ) |
| vector<T>& lti::vector< T >::add | ( | const vector< T > & | other | ) |
| vector<T>& lti::vector< T >::addScaled | ( | const vector< T > & | first, | |
| const T | b, | |||
| const vector< T > & | second | |||
| ) |
Leave the addition of the first vector and the second vector scaled with the given factor in this vector.
The vectors must be of the same types and dimensions. Let A be the first vector and B the second vector with corresponding scaling factor b, further C this vector, then this method performs:
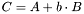 If both vectors have different size, an assertion will be thrown
If both vectors have different size, an assertion will be thrown
| first | the first vector to be added after scaling | |
| b | scaling factor for second | |
| second | the second vector to be added after scaling |
| vector<T>& lti::vector< T >::addScaled | ( | const T | a, | |
| const vector< T > & | first, | |||
| const T | b, | |||
| const vector< T > & | second | |||
| ) |
Leave the scaled sum of two vectors in this vector.
The vectors must be of the same types and dimensions. Let A be the first vector and B the second vector with corresponding scaling factors a and b, further C this vector, then this method performs:
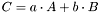 If both vectors have different size, an assertion will be thrown
If both vectors have different size, an assertion will be thrown
| a | scaling factor for first | |
| first | the first vector to be added after scaling | |
| b | scaling factor for second | |
| second | the second vector to be added after scaling |
| vector<T>& lti::vector< T >::addScaled | ( | const T | b, | |
| const vector< T > & | other | |||
| ) |
| virtual mathObject* lti::vector< T >::clone | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
create a clone of this genericVector
Reimplemented from lti::genericVector< T >.
Reimplemented in lti::kernel1D< T >, lti::kernel1D< double >, and lti::kernel1D< float >.
| vector<T>& lti::vector< T >::divide | ( | const vector< T > & | other, | |
| const T | cst | |||
| ) |
| vector<T>& lti::vector< T >::divide | ( | const T | cst | ) |
| T lti::vector< T >::dot | ( | const vector< T > & | other | ) | const |
| vector<T>& lti::vector< T >::edivide | ( | const vector< T > & | other, | |
| const T | cst | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Divide the other vector with a constant and leave the result here.
Returns a reference to this vector.
synonym for divide(const vector<T>& other,const T cst).
| other | the vector to be divide by the constant value | |
| cst | the elements of the vector will be divided with this constant |
| vector<T>& lti::vector< T >::edivide | ( | const T | cst | ) | [inline] |
| vector<T>& lti::vector< T >::edivide | ( | const vector< T > & | first, | |
| const vector< T > & | second | |||
| ) |
| vector<T>& lti::vector< T >::edivide | ( | const vector< T > & | other | ) |
Elementwise division.
Each element of this vector will be divided by the elements of the other vector and the result will be left in this object! The returned vector is this object! If both vectors have different size, an assertion will be thrown
| other | the other vector to be divided by |
| vector<T>& lti::vector< T >::emultiply | ( | const vector< T > & | first, | |
| const vector< T > & | second | |||
| ) |
Elementwise multiplication.
This vector will contain the elementwise multiplication of the elements in first and second. If both vectors have different size, an assertion will be thrown
| first | the first vector | |
| second | the second vector will be multiplied with the first vector |
| vector<T>& lti::vector< T >::emultiply | ( | const vector< T > & | other | ) |
Elementwise multiplication.
Each element of this vector will be multiplied with the elements of the other vector and the result will be left in this object! If both vectors have different size, an assertion will be thrown The return vector is this object!
| other | the other vector to be multiplied with |
| void lti::vector< T >::getExtremes | ( | T & | theMinimum, | |
| T & | theMaximum | |||
| ) | const |
get the extremes of the vector (smallest and biggest elements)
| void lti::vector< T >::getIndexOfExtremes | ( | int & | theIdxMinimum, | |
| int & | theIdxMaximum | |||
| ) | const |
get the indices of the extremes of the vector (smallest and biggest elements)
| int lti::vector< T >::getIndexOfMaximum | ( | ) | const |
get the index of the biggest element of the vector
| int lti::vector< T >::getIndexOfMinimum | ( | ) | const |
get the index of the smallest element of the vector
| const char* lti::vector< T >::getTypeName | ( | void | ) | const [inline, virtual] |
returns the name of this class: "vector"
Reimplemented from lti::genericVector< T >.
Reimplemented in lti::kernel1D< T >, lti::array< T >, lti::kernel1D< double >, lti::kernel1D< float >, lti::array< double >, lti::array< float >, and lti::array< int >.
| T lti::vector< T >::maximum | ( | ) | const |
get the biggest element of the vector
Referenced by lti::SOFM2DVisualizer::drawClasses().
| T lti::vector< T >::minimum | ( | ) | const |
get the smallest element of the vector
| vector<T>& lti::vector< T >::multiply | ( | const vector< T > & | other, | |
| const T | cst | |||
| ) |
Multiply the other vector with a constant and leave the result here.
Returns a reference to this vector. If both vectors have different size, an assertion will be thrown
| other | the other vector to be multiplied with the constant value | |
| cst | constant scalar to be multiplied with the other vector. |
| vector<T>& lti::vector< T >::multiply | ( | const T | cst | ) |
| vector<T>& lti::vector< T >::operator*= | ( | const T | cst | ) |
| vector<T>& lti::vector< T >::operator+= | ( | const vector< T > & | other | ) |
Alias for add(const vector<T>& other).
| vector<T>& lti::vector< T >::operator+= | ( | const T | cst | ) |
Alias for add(const T cst).
| vector<T>& lti::vector< T >::operator-= | ( | const T | cst | ) |
Alias for subtract(const T& cst).
| vector<T>& lti::vector< T >::operator-= | ( | const vector< T > & | other | ) |
Alias for substract(const vector<T>& other) If both vectors have different size, an assertion will be thrown.
| vector<T>& lti::vector< T >::operator/= | ( | const T | cst | ) |
Alias for divide(const T& cst).
| bool lti::vector< T >::prettyCloseTo | ( | const vector< T > & | other, | |
| const T & | tolerance | |||
| ) | const |
compare this vector with other, and use the given tolerance to determine if the value of each element of the other vector approximately equals the values of the actual vector elements.
An element x is approximately equal to another element y with a tolerance t, if following equation holds: x-t < y < x+t
| other | the other vector to be compared with | |
| tolerance | the tolerance to be used |
| T lti::vector< T >::productOfElements | ( | ) | const |
calculate the product of all elements of the vector.
This member can be used with classes which define the operator '*='
| vector<T>& lti::vector< T >::subtract | ( | const vector< T > & | first, | |
| const vector< T > & | second | |||
| ) |
| vector<T>& lti::vector< T >::subtract | ( | const vector< T > & | other | ) |
| vector<T>& lti::vector< T >::subtract | ( | const vector< T > & | other, | |
| const T | cst | |||
| ) |
| vector<T>& lti::vector< T >::subtract | ( | const T | cst | ) |
| T lti::vector< T >::sumOfElements | ( | ) | const |
calculate the sum of all elements of the vector.
This member can be used with classes which define the operator '+='
Referenced by lti::SOFM2DVisualizer::uMatrix().