

|
latest version v1.9 - last update 10 Apr 2010 |
|
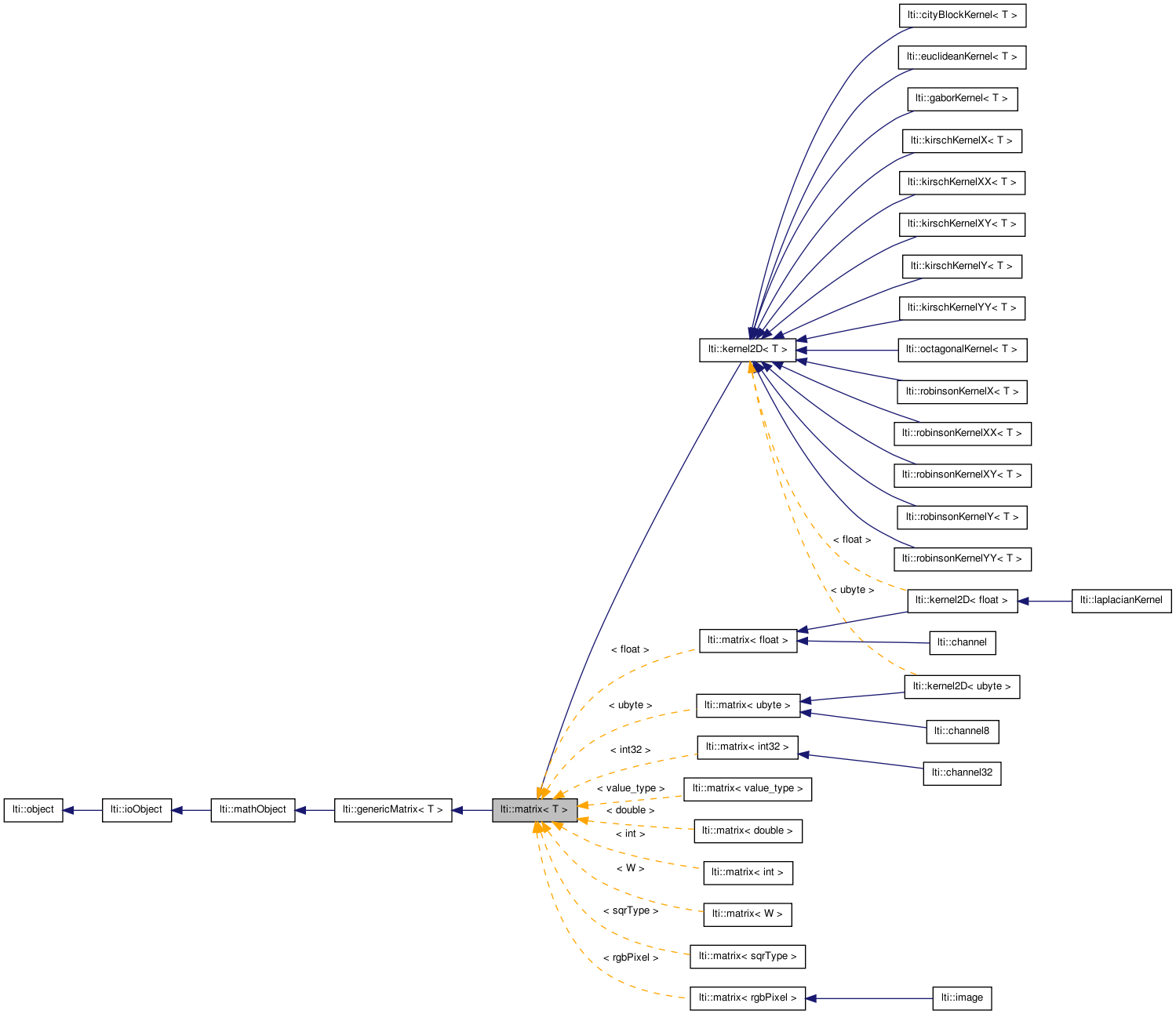
Mathematical matrix container class. More...
#include <ltiMatrix.h>
Public Types | |
| typedef T | value_type |
| typedef ipoint | size_type |
Public Member Functions | |
| matrix () | |
| matrix (const int rows, const int cols, const T &iniValue=T()) | |
| matrix (const int rows, const int cols, const T data[]) | |
| matrix (const ipoint &size, const T &iniValue=T()) | |
| matrix (const matrix< T > &other, const int fromRow=0, const int toRow=MaxInt32, const int fromCol=0, const int toCol=MaxInt32) | |
| matrix (const bool copyData, matrix< T > &other, const int fromRow=0, const int toRow=MaxInt32, const int fromCol=0, const int toCol=MaxInt32) | |
| matrix (const bool init, const int rows, const int cols) | |
| matrix (const bool init, const ipoint &size) | |
| matrix (const matrix< T > &other, const genericVector< int > &rows) | |
| virtual | ~matrix () |
| virtual const char * | getTypeName () const |
| vector< T > & | getRow (const int row) |
| const vector< T > & | getRow (const int row) const |
| vector< T > & | operator[] (const int row) |
| const vector< T > & | operator[] (const int row) const |
| vector< T > | getRowCopy (const int row) const |
| void | getRowCopy (const int row, vector< T > &theRow) const |
| vector< T > | getColumnCopy (const int col) const |
| void | getColumnCopy (const int col, vector< T > &theCol) const |
| vector< T > | getDiagonal () const |
| void | getDiagonal (vector< T > &diag) const |
| matrix< T > & | copy (const matrix< T > &other) |
| matrix< T > & | copy (const matrix< T > &other, const int fromRow, const int toRow=MaxInt32, const int fromCol=0, const int toCol=MaxInt32) |
| matrix< T > & | copy (const matrix< T > &other, const irectangle &window) |
| matrix< T > & | copy (const matrix< T > &other, const vector< int > &idx, bool rows=true) |
| template<class U > | |
| matrix< T > & | castFrom (const matrix< U > &other) |
| virtual mathObject * | clone () const |
| bool | prettyCloseTo (const matrix< T > &other, const T &tolerance) const |
| matrix< T > & | operator= (const matrix< T > &other) |
Apply Methods | |
| matrix< T > & | apply (T(*function)(T)) |
| matrix< T > & | apply (const matrix< T > &other, T(*function)(T)) |
| matrix< T > & | apply (T(*function)(const T &)) |
| matrix< T > & | apply (const matrix< T > &other, T(*function)(const T &)) |
| matrix< T > & | apply (const matrix< T > &other, T(*function)(const T &, const T &)) |
| matrix< T > & | apply (const matrix< T > &other, T(*function)(T, T)) |
| matrix< T > & | apply (const matrix< T > &a, const matrix< T > &b, T(*function)(const T &, const T &)) |
| matrix< T > & | apply (const matrix< T > &a, const matrix< T > &b, T(*function)(T, T)) |
Arithmetical Operations | |
| matrix< T > & | add (const matrix< T > &other) |
| matrix< T > & | add (const matrix< T > &a, const matrix< T > &b) |
| matrix< T > & | add (const T value) |
| matrix< T > & | add (const matrix< T > &other, const T value) |
| matrix< T > & | operator+= (const T value) |
| matrix< T > & | operator+= (const matrix< T > &other) |
| matrix< T > | operator+ (const matrix< T > &other) const |
| matrix< T > | operator+ (const T value) const |
| matrix< T > & | addScaled (const T b, const matrix< T > &other) |
| matrix< T > & | addScaled (const matrix< T > &matA, const T b, const matrix< T > &matB) |
| matrix< T > & | addScaled (const T a, const matrix< T > &first, const T b, const matrix< T > &second) |
| matrix< T > & | subtract (const matrix< T > &other) |
| matrix< T > & | subtract (const matrix< T > &a, const matrix< T > &b) |
| matrix< T > & | subtract (const T value) |
| matrix< T > & | subtract (const matrix< T > &other, const T value) |
| matrix< T > & | operator-= (const T value) |
| matrix< T > & | operator-= (const matrix< T > &other) |
| matrix< T > & | multiply (const matrix< T > &other) |
| matrix< T > & | multiply (const matrix< T > &first, const matrix< T > &second) |
| vector< T > & | multiply (const vector< T > &other, vector< T > &result) const |
| vector< T > & | multiply (vector< T > &srcdest) const |
| matrix< T > & | multiply (const T value) |
| matrix< T > & | multiply (const matrix< T > &other, const T value) |
| matrix< T > & | operator*= (const matrix< T > &other) |
| matrix< T > & | operator*= (const T value) |
| vector< T > & | leftMultiply (const vector< T > &vct, vector< T > &result) const |
| vector< T > & | leftMultiply (vector< T > &srcDest) const |
| matrix< T > & | leftMultiply (const matrix< T > &mat) |
| matrix< T > & | divide (const T value) |
| matrix< T > & | divide (const matrix< T > &other, const T value) |
| matrix< T > & | operator/= (const T value) |
| matrix< T > & | emultiply (const matrix< T > &other) |
| matrix< T > & | emultiply (const matrix< T > &a, const matrix< T > &b) |
| matrix< T > & | edivide (const matrix< T > &other) |
| matrix< T > & | edivide (const matrix< T > &a, const matrix< T > &b) |
| matrix< T > & | outerProduct (const vector< T > &a, const vector< T > &b) |
| matrix< T > & | transpose () |
| matrix< T > & | transpose (const matrix< T > &other) |
| T | sumOfElements () const |
| T | minimum () const |
| ipoint | getIndexOfMinimum () const |
| T | maximum () const |
| ipoint | getIndexOfMaximum () const |
| void | getExtremes (T &theMinimum, T &theMaximum) const |
| void | getIndexOfExtremes (point &theIdxMinimum, ipoint &theIdxMaximum) const |
| void | setIdentity (const T scale=T(1)) |
| T | trace () const |
Protected Member Functions | |
| virtual genericVector< T > * | allocRows (const int n) |
Mathematical matrix container class.
The lti::matrix class allows the representation of n x m matrices. The rows will be indexed between 0 and n-1, and the columns between 0 and m-1.
All types defined in ltiTypes.h use static members and can be contained by the lti::vector and lti::matrix classes.
The matrix class is a container class implemented as template.
If you need to create a matrix of floats with 20 rows and 15 columns, all elements initialized with an initial value of 4.27 just create it:
lti::matrix<float> myMat(20,15,4.27f) // creates matrix with 300 elements // all initialized with 4.27f
To access the matrix elements use the access operators. There are many possibilities. With at(const int row, const int col) is possible to access an element directly. With at(const int row) you can get the row vector. You cannot for instance resize nor change the memory referenced in this vector (see lti::vector::resize). For example:
float accu = 0; // initialize accumulator lti::matrix<float> myMat(20,15,4.27f) lti::vector<float> myVct; for (int j = 0; j < myMat.rows(); j++) { for (int i = 0; i < myMat.columns(); i++) { tmp += myMat.at(j,i); // access each element of the matrix: // j is the row and i the column } } myMat.getRowCopy(5,myVct); // copy the sixth row in myVct! myVct.resize(6); // Valid, the vector has its own memory! myMat.at(5).resize(6) // ERROR!! the vector is not resizable!
The image representation in the LTI-Lib is based on the lti::matrix class. It is quite confusing to use first the y-coordinate and then the x-coordinate to access the image elements. To avoid confusion use the lti::point class to access the elements of the matrix:
lti::channel8 aChannel(20,15); // creates an 8bit image lti::channel8::value_type tmp; // tmp is of the element type of the // channel8! lti::point p; for (p.y = 0; p.y < aChannel.rows(); p.y++) { for (p.x = 0; p.x < aChannel.columns(); p.x++) { tmp += aChannel.at(p); // access each element of the matrix: // equivalent to: tmp += aChannel.at(p.y,p.x)! } }
The parent class is lti::genericMatrix and provides many memory management options.
The matrix has following methods:
| typedef ipoint lti::matrix< T >::size_type |
return type of the size() member
Reimplemented from lti::genericMatrix< T >.
| typedef T lti::matrix< T >::value_type |
type of the contained data
Reimplemented from lti::genericMatrix< T >.
| lti::matrix< T >::matrix | ( | ) |
default constructor creates an empty matrix
| lti::matrix< T >::matrix | ( | const int | rows, | |
| const int | cols, | |||
| const T & | iniValue = T() | |||
| ) |
| lti::matrix< T >::matrix | ( | const int | rows, | |
| const int | cols, | |||
| const T | data[] | |||
| ) |
this constructor creates a connected rows x cols Matrix and initializes all elements with the data pointed by data.
The first cols-elements of the data will be copied on the first row, the next ones on the second row and so on.
| lti::matrix< T >::matrix | ( | const ipoint & | size, | |
| const T & | iniValue = T() | |||
| ) |
this constructor creates a connected size.y x size.x Matrix and initializes all elements with iniValue
| size | lti::point with the size of the matrix (size.x is the number of columns and size.y the number of rows) | |
| iniValue | all elements will be initialized with this value |
| lti::matrix< T >::matrix | ( | const matrix< T > & | other, | |
| const int | fromRow = 0, |
|||
| const int | toRow = MaxInt32, |
|||
| const int | fromCol = 0, |
|||
| const int | toCol = MaxInt32 | |||
| ) |
copy constructor.
create this matrix as a connected copy of another matrix for this const version, the data will be always copied! It is also possible to create a copy of a submatrix of another matrix.
| other | the matrix to be copied. | |
| fromRow | initial row of the other matrix to be copied | |
| toRow | last row to be copied of the other matrix | |
| fromCol | initial column of the other matrix to be copied | |
| toCol | last column to be copied of the other matrix |
Example:
lti::matrix<int> m(4,6,0); // integer matrix with 25 elements // ... // initialize Matrix with: // 0 1 2 3 4 5 // 2 1 5 4 0 3 // 1 2 1 2 3 2 // 3 3 2 1 2 3 lti::matrix<int> sm(m,0,2,1,3) // last line will lead to // following contents in sm: // 1 2 3 // 1 5 4 // 2 1 2
| lti::matrix< T >::matrix | ( | const bool | copyData, | |
| matrix< T > & | other, | |||
| const int | fromRow = 0, |
|||
| const int | toRow = MaxInt32, |
|||
| const int | fromCol = 0, |
|||
| const int | toCol = MaxInt32 | |||
| ) |
copy constructor (reference to a submatrix).
creates submatrix of another matrix.
if copyData == true, the new object has its own data (equivalent to previous copy constructor).
if copyData == false, the new object has references to the other matrix, which means that the data is not necessarily consecutive. (This will not be a connected but a lined matrix)
Those algorithms which use direct access to the matrix memory block should check first if the memory lies in a consecutive block! (see getMode())
| copyData | should the data of the other matrix be copied or not | |
| other | the matrix with the data to be copied or to be shared | |
| fromRow | initial row of the other matrix to be copied | |
| toRow | last row to be copied of the other matrix | |
| fromCol | initial column of the other matrix to be copied | |
| toCol | last column to be copied of the other matrix |
| lti::matrix< T >::matrix | ( | const bool | init, | |
| const int | rows, | |||
| const int | cols | |||
| ) |
If init is true this constructor is equivalent to calling matrix(const int rows, const int cols), and thus initializing all elements with T().
However, in some cases the elements need not be initialized during construction, since complex initializion is required. Especially for large matrices, the unnecessary constructor initialization is very time consuming.
If init is false, memory is allocated but no initialization takes place. Thus the following is equivalent:
matrix<int> a(false,100,100); matrix<int> a; a.resize(100,100,0,false,false);
| lti::matrix< T >::matrix | ( | const bool | init, | |
| const ipoint & | size | |||
| ) |
If init is true this constructor is equivalent to calling matrix(const int rows, const int cols), and thus initializing all elements with T().
However, in some cases the elements need not be initialized during construction, since complex initializion is required. Especially for large matrices, the unnecessary constructor initialization is very time consuming.
If init is false, memory is allocated but no initialization takes place. Thus the following is equivalent:
matrix<int> a(false,100,100); matrix<int> a; a.resize(100,100,0,false,false);
| lti::matrix< T >::matrix | ( | const matrix< T > & | other, | |
| const genericVector< int > & | rows | |||
| ) |
copy constructor.
create this matrix as a connected copy of another matrix taking only the rows indicated by the vector. for this const version, the data will be always copied! Multiple occurence of one row index in rows is allowed.
| other | the matrix to be copied. | |
| rows | inidices of the rows to be copied |
Example:
lti::vector<int> rows(2); // initialize with // 1 3 lti::matrix<int> m(4,6,0); // integer matrix with 25 elements // ... // initialize Matrix with: // 0 1 2 3 4 5 // 2 1 5 4 0 3 // 1 2 1 2 3 2 // 3 3 2 1 2 3 lti::matrix<int> sm(m,rows) // last line will lead to // following contents in sm: // 2 1 5 4 0 3 // 3 3 2 1 2 3
| virtual lti::matrix< T >::~matrix | ( | ) | [virtual] |
destructor
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::add | ( | const matrix< T > & | other, | |
| const T | value | |||
| ) |
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::add | ( | const T | value | ) |
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::add | ( | const matrix< T > & | a, | |
| const matrix< T > & | b | |||
| ) |
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::add | ( | const matrix< T > & | other | ) |
add other matrix to this matrix, and leave result here
| other | the matrix to be added with |
Referenced by lti::matrix< ubyte >::operator+=().
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::addScaled | ( | const T | a, | |
| const matrix< T > & | first, | |||
| const T | b, | |||
| const matrix< T > & | second | |||
| ) |
Leave the scaled sum of two matrices in this matrix.
The matrices must be of the same types and dimensions. Let 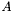 be the first matrix and
be the first matrix and 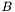 the second matrix with corresponding scaling factors
the second matrix with corresponding scaling factors 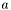 and
and 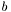 , further
, further 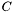 this matrix, then this method performs:
this matrix, then this method performs:
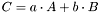
| a | scaling factor for first | |
| first | the first matrix to be added after scaling | |
| b | scaling factor for second | |
| second | the second matrix to be added after scaling |
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::addScaled | ( | const matrix< T > & | matA, | |
| const T | b, | |||
| const matrix< T > & | matB | |||
| ) |
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::addScaled | ( | const T | b, | |
| const matrix< T > & | other | |||
| ) |
| virtual genericVector<T>* lti::matrix< T >::allocRows | ( | const int | n | ) | [inline, protected, virtual] |
Allocate n number of rows or the appropriate type.
Reimplemented from lti::genericMatrix< T >.
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::apply | ( | const matrix< T > & | a, | |
| const matrix< T > & | b, | |||
| T(*)(T, T) | function | |||
| ) |
a two-parameter C-function receives the i-th elements of both given matrices and leaves the result here.
Note that both matrices must have the same size!
| a | the first matrix | |
| b | the second matrix | |
| function | a pointer to C-function with two parameters |
Reimplemented from lti::genericMatrix< T >.
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::apply | ( | const matrix< T > & | a, | |
| const matrix< T > & | b, | |||
| T(*)(const T &, const T &) | function | |||
| ) |
a two-parameter C-function receives the i-th elements of both given matrices and leaves the result here.
Note that both matrices must have the same size!
| a | the first matrix | |
| b | the second matrix | |
| function | a pointer to C-function with two parameters |
Reimplemented from lti::genericMatrix< T >.
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::apply | ( | const matrix< T > & | other, | |
| T(*)(T, T) | function | |||
| ) |
a two-parameter C-function receives the i-th elements of this and the given matrix and the result will be left in this matrix.
Note that both matrices must have the same size!
| other | the second matrix to be considered (the first matrix will be this object!) | |
| function | a pointer to C-function with two parameters |
Reimplemented from lti::genericMatrix< T >.
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::apply | ( | const matrix< T > & | other, | |
| T(*)(const T &, const T &) | function | |||
| ) |
a two-parameter C-function receives the i-th elements of this and the given matrix and the result will be left in this matrix.
Note that both matrices must have the same size!
| other | the second matrix to be considered (the first matrix will be this object!) | |
| function | a pointer to C-function with two parameters |
Reimplemented from lti::genericMatrix< T >.
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::apply | ( | const matrix< T > & | other, | |
| T(*)(const T &) | function | |||
| ) |
applies a C-function to each element of the other matrix
| other | the matrix which elements will go through the given function. | |
| function | a pointer to a C-function |
Reimplemented from lti::genericMatrix< T >.
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::apply | ( | T(*)(const T &) | function | ) |
applies a C-function to each element of the matrix.
| function | a pointer to a C-function |
Reimplemented from lti::genericMatrix< T >.
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::apply | ( | const matrix< T > & | other, | |
| T(*)(T) | function | |||
| ) |
applies a C-function to each element of the other matrix
| other | the matrix which elements will go through the given function. | |
| function | a pointer to a C-function |
Reimplemented from lti::genericMatrix< T >.
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::apply | ( | T(*)(T) | function | ) |
applies a C-function to each element of the matrix.
| function | a pointer to a C-function |
Reimplemented from lti::genericMatrix< T >.
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::castFrom | ( | const matrix< U > & | other | ) | [inline] |
copy the other matrix by casting each of its elements
| other | The matrix to be casted Example:
lti::matrix<int> matA(10,10,1);// a matrix of integers lti::matrix<double> matB; // a matrix of doubles matB.castFrom(matA); // this will copy matA in matB!! |
Reimplemented from lti::genericMatrix< T >.
Reimplemented in lti::channel, lti::channel8, lti::channel32, and lti::kernel2D< T >.
Referenced by lti::fillPattern::setMask().
| virtual mathObject* lti::matrix< T >::clone | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
create a clone of this matrix
Reimplemented from lti::genericMatrix< T >.
Reimplemented in lti::image, lti::channel, lti::channel8, lti::channel32, lti::kernel2D< T >, lti::kernel2D< float >, and lti::kernel2D< ubyte >.
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::copy | ( | const matrix< T > & | other, | |
| const vector< int > & | idx, | |||
| bool | rows = true | |||
| ) | [inline] |
assigment operator.
copy the contents of the specified rows/columns of other into this object. Multiple occurence of one row/column index in idx is allowed. If the argument rows is true, idx specifies rows, if false idx specifies columns.
The result of the copy is always a connected matrix. I.e. you cannot copy the sub-matrix property of another matrix.
| other | the other matrix to be copied | |
| idx | indices of the rows to be copied. | |
| rows | if true works on rows, else on columns |
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::copy | ( | const matrix< T > & | other, | |
| const irectangle & | window | |||
| ) | [inline] |
assigment operator.
copy the contents of other in this object.
The result of the copy is always a connected matrix. I.e. you cannot copy the sub-matrix property of another matrix.
| other | the other matrix to be copied | |
| window | rectangle define the copy area |
Reimplemented from lti::genericMatrix< T >.
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::copy | ( | const matrix< T > & | other, | |
| const int | fromRow, | |||
| const int | toRow = MaxInt32, |
|||
| const int | fromCol = 0, |
|||
| const int | toCol = MaxInt32 | |||
| ) | [inline] |
assigment operator.
copy the contents of other in this object.
The result of the copy is always a connected matrix. I.e. you cannot copy the sub-matrix property of another matrix.
| other | the other matrix to be copied | |
| fromRow | initial row of the other matrix to be copied | |
| toRow | last row to be copied of the other matrix | |
| fromCol | initial column of the other matrix to be copied | |
| toCol | last column to be copied of the other matrix |
Reimplemented from lti::genericMatrix< T >.
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::copy | ( | const matrix< T > & | other | ) | [inline] |
assigment operator.
copy the contents of other in this object.
The result of the copy is always a connected matrix. I.e. you cannot copy the sub-matrix property of another matrix.
| other | the other matrix to be copied |
Reimplemented from lti::genericMatrix< T >.
Reimplemented in lti::kernel2D< T >, and lti::kernel2D< float >.
Referenced by lti::earthMoversDistance< W, C, D >::parameters::copy(), lti::medianFilter::realMedian(), and lti::SOFM2DVisualizer::uMatrix().
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::divide | ( | const matrix< T > & | other, | |
| const T | value | |||
| ) |
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::divide | ( | const T | value | ) |
divide the elements of the matrix by a constant value, and leave the result here
| value | the constant value (divisor) |
Referenced by lti::SOFM2DVisualizer::drawHits(), and lti::matrix< ubyte >::operator/=().
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::edivide | ( | const matrix< T > & | a, | |
| const matrix< T > & | b | |||
| ) |
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::edivide | ( | const matrix< T > & | other | ) |
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::emultiply | ( | const matrix< T > & | a, | |
| const matrix< T > & | b | |||
| ) |
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::emultiply | ( | const matrix< T > & | other | ) |
| void lti::matrix< T >::getColumnCopy | ( | const int | col, | |
| vector< T > & | theCol | |||
| ) | const [inline] |
return genericMatrix-column as a vector.
This method copies the data of the genericMatrix, therefore is not as fast as getRow()
| col | the number of the column to be copied | |
| theCol | a vector, where the column vector of the genericMatrix should be copied. |
| vector<T> lti::matrix< T >::getColumnCopy | ( | const int | col | ) | const [inline] |
return matrix-column as a vector.
This method copies the data of the matrix, therefore is not as fast as getRow()
| col | the number of the column to be copied |
Reimplemented from lti::genericMatrix< T >.
Referenced by lti::SOFM2DVisualizer::componentPlane().
| void lti::matrix< T >::getDiagonal | ( | vector< T > & | diag | ) | const [inline] |
Return the diagonal elements of the genericMatrix as vector.
This method copies the diagonal elements of the genericMatrix into the vector. If the genericMatrix is non-symmetrical, the vector will be of dimension min(rows(),columns()).
| diag | a vector, where the diagonal of the genericMatrix should be copied. |
| vector<T> lti::matrix< T >::getDiagonal | ( | ) | const [inline] |
| void lti::matrix< T >::getExtremes | ( | T & | theMinimum, | |
| T & | theMaximum | |||
| ) | const |
get the extremes of the matrix (smallest and biggest elements)
| void lti::matrix< T >::getIndexOfExtremes | ( | point & | theIdxMinimum, | |
| ipoint & | theIdxMaximum | |||
| ) | const |
get the indices of the extremes of the matrix (smallest and biggest elements)
| ipoint lti::matrix< T >::getIndexOfMaximum | ( | ) | const |
get the index of the biggest element of the matrix
| ipoint lti::matrix< T >::getIndexOfMinimum | ( | ) | const |
get the index of the smallest element of the matrix
| const vector<T>& lti::matrix< T >::getRow | ( | const int | row | ) | const [inline] |
return matrix-row as a const vector.
This method works fast, since it returns a reference to the row vector. The data will NOT be copied.
| row | the row to be accessed |
Reimplemented from lti::genericMatrix< T >.
| vector<T>& lti::matrix< T >::getRow | ( | const int | row | ) | [inline] |
return matrix-row as a vector.
This method works fast, since it returns a reference to the row vector. The data will NOT be copied.
| row | the row to be accessed |
Reimplemented from lti::genericMatrix< T >.
Referenced by lti::decimation::apply(), lti::matrix< ubyte >::castFrom(), lti::SOFM2DVisualizer::drawClasses(), lti::SOFM2DVisualizer::drawHits(), and lti::SOFM2DVisualizer::uMatrix().
| void lti::matrix< T >::getRowCopy | ( | const int | row, | |
| vector< T > & | theRow | |||
| ) | const [inline] |
Copy a row vector in the given parameter.
This method copies the data of a given row of the genericMatrix in the given vector.
| row | the number of the row to be copied | |
| theRow | the vector, where the data will be copied |
| vector<T> lti::matrix< T >::getRowCopy | ( | const int | row | ) | const [inline] |
| virtual const char* lti::matrix< T >::getTypeName | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
returns the name of this class: "matrix"
Reimplemented from lti::genericMatrix< T >.
Reimplemented in lti::image, lti::channel, lti::channel8, lti::channel32, lti::kernel2D< T >, lti::kernel2D< float >, and lti::kernel2D< ubyte >.
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::leftMultiply | ( | const matrix< T > & | mat | ) |
| vector<T>& lti::matrix< T >::leftMultiply | ( | vector< T > & | srcDest | ) | const |
multiply the given vector srcdest with this matrix, and save the result in the same vector.
The given vector will be interpreted as a row-vector (or a transposed column vector).
| srcDest | the vector to be multiplied with, and where the result must be written. |
| vector<T>& lti::matrix< T >::leftMultiply | ( | const vector< T > & | vct, | |
| vector< T > & | result | |||
| ) | const |
| T lti::matrix< T >::maximum | ( | ) | const |
get the biggest element of the matrix
Referenced by lti::SOFM2DVisualizer::drawHits().
| T lti::matrix< T >::minimum | ( | ) | const |
get the smallest element of the matrix
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::multiply | ( | const matrix< T > & | other, | |
| const T | value | |||
| ) |
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::multiply | ( | const T | value | ) |
| vector<T>& lti::matrix< T >::multiply | ( | vector< T > & | srcdest | ) | const |
multiply this matrix with a vector and leave the result in same vector (In-Place Method) A reference to the vector is returned.
| srcdest | the vector to be multiplied with. Its dimension must be equal to the number of columns of the matrix. The result vector will be left here too, and the resulting size will be the number of rows of the matrix. |
| vector<T>& lti::matrix< T >::multiply | ( | const vector< T > & | other, | |
| vector< T > & | result | |||
| ) | const |
multiply this matrix with a vector and leave the result in result.
A reference to result is returned.
| other | the vector to be multiplied with. Its dimension must be equal to the number of columns of the matrix. | |
| result | the resulting vector. It will have a number of dimensions equal to the number of rows of the matrix. |
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::multiply | ( | const matrix< T > & | first, | |
| const matrix< T > & | second | |||
| ) |
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::multiply | ( | const matrix< T > & | other | ) |
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::operator*= | ( | const T | value | ) | [inline] |
alias for multiply(const T& value)
| value | the constant value to be multiplied with |
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::operator*= | ( | const matrix< T > & | other | ) | [inline] |
| matrix<T> lti::matrix< T >::operator+ | ( | const T | value | ) | const |
| matrix<T> lti::matrix< T >::operator+ | ( | const matrix< T > & | other | ) | const |
add other matrix to this matrix and leave the result in a new matrix.
This object is not changed.
| other | the other matrix to be added with. |
Note that the use of this operator is not as efficient as the use of the add() methods, in which the programmer can decide when to use temporal and when not...
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::operator+= | ( | const matrix< T > & | other | ) | [inline] |
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::operator+= | ( | const T | value | ) | [inline] |
alias for add(const T value)
| value | a constant value to be added to all matrix elements |
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::operator-= | ( | const matrix< T > & | other | ) | [inline] |
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::operator-= | ( | const T | value | ) | [inline] |
alias for subtract(const T value)
| value | a constant value to be subtracted from all matrix elements |
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::operator/= | ( | const T | value | ) | [inline] |
alias for divide(const T& value)
| value | the constant value to be divided by |
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::operator= | ( | const matrix< T > & | other | ) | [inline] |
assigment operator (alias for copy(other)).
| other | the matrix to be copied |
Reimplemented from lti::genericMatrix< T >.
| const vector<T>& lti::matrix< T >::operator[] | ( | const int | row | ) | const [inline] |
alias for getRow()
Reimplemented from lti::genericMatrix< T >.
| vector<T>& lti::matrix< T >::operator[] | ( | const int | row | ) | [inline] |
alias for getRow()
Reimplemented from lti::genericMatrix< T >.
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::outerProduct | ( | const vector< T > & | a, | |
| const vector< T > & | b | |||
| ) |
outer-product of two vectors.
The result will be left in this matrix. The dimensions of this matrix will change if needed. The outer product of two column vectors is defined as 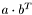
| a | first vector (will determine the number of rows) | |
| b | second vector (will determine the number of columns) |
| bool lti::matrix< T >::prettyCloseTo | ( | const matrix< T > & | other, | |
| const T & | tolerance | |||
| ) | const |
compare this matrix with other, and use the given tolerance to determine if the value of each element of the other matrix approximately equals the values of the actual matrix elements.
An element x is approximately equal to another element y with a tolerance t, if following equation holds: x-t < y < x+t
| other | the other matrix to be compared with | |
| tolerance | the tolerance to be used |
| void lti::matrix< T >::setIdentity | ( | const T | scale = T(1) |
) |
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::subtract | ( | const matrix< T > & | other, | |
| const T | value | |||
| ) |
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::subtract | ( | const T | value | ) |
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::subtract | ( | const matrix< T > & | a, | |
| const matrix< T > & | b | |||
| ) |
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::subtract | ( | const matrix< T > & | other | ) |
subtract other matrix from this matrix, and leave result here.
| other | the matrix to be subtracted |
Referenced by lti::matrix< ubyte >::operator-=().
| T lti::matrix< T >::sumOfElements | ( | ) | const |
calculate the sum of all elements of the matrix.
This member can be used with classes which define the operator '+='
Reimplemented in lti::channel8.
| T lti::matrix< T >::trace | ( | ) | const |
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::transpose | ( | const matrix< T > & | other | ) |
| matrix<T>& lti::matrix< T >::transpose | ( | ) |