

|
latest version v1.9 - last update 10 Apr 2010 |
|
Histogram template class. More...
#include <ltiHistogram.h>
Public Types | |
| typedef vector< T >::iterator | iterator |
| typedef vector< T >::const_iterator | const_iterator |
Public Member Functions | |
| thistogram () | |
| thistogram (const int &dimensions, const int &cells) | |
| thistogram (const int &dimensions, const ivector &cells) | |
| thistogram (const thistogram< T > &other) | |
| virtual | ~thistogram () |
| const char * | getTypeName () const |
| int | dimensions () const |
| int | cellsInDimension (const int &dimension) const |
| const ivector & | cellsPerDimension () const |
| const ivector & | getFirstCell () const |
| const ivector & | getLastCell () const |
| const_iterator | begin () const |
| iterator | begin () |
| const_iterator | end () const |
| iterator | end () |
| void | resize (const int &dimensions, const int &cells) |
| void | resize (const int &dimensions, const ivector &cells) |
| void | clear () |
| void | initialize (const T &value=T(0)) |
| const T & | getNumberOfEntries () const |
| void | setNumberOfEntries (const T &newNumberOfEntries) |
| void | updateNumberOfEntries () |
| void | fill (const T &iniValue, const ivector &from=ivector(), const ivector &to=ivector()) |
| const T & | at (const ivector &x) const |
| T & | at (const ivector &x) |
| const T & | put (const ivector &x, const T &increment=T(1)) |
| double | getProbability (const ivector &x) const |
Copy and Duplication methods | |
| thistogram< T > & | copy (const thistogram< T > &other) |
| thistogram< T > & | operator= (const thistogram< T > &other) |
| template<class U > | |
| thistogram< T > & | castFrom (const thistogram< U > &other) |
| virtual mathObject * | clone () const |
| void | detach (thistogram< T > &receiver) |
Comparison methods | |
| bool | equals (const thistogram< T > &other) const |
| bool | operator== (const thistogram< T > &other) const |
| bool | prettyCloseTo (const thistogram< T > &other, const T &tolerance) const |
| thistogram< T > & | apply (T(*function)(T)) |
| thistogram< T > & | apply (T(*function)(const T &)) |
Arithmetical operations | |
| thistogram< T > & | emultiply (const thistogram< T > &other) |
| thistogram< T > & | emultiply (const thistogram< T > &first, const thistogram< T > &second) |
| thistogram< T > & | add (const thistogram< T > &other) |
| thistogram< T > & | add (const thistogram< T > &first, const thistogram< T > &second) |
| thistogram< T > & | operator+= (const thistogram< T > &other) |
| thistogram< T > & | subtract (const thistogram< T > &other) |
| thistogram< T > & | subtract (const thistogram< T > &first, const thistogram< T > &second) |
| thistogram< T > & | operator-= (const thistogram< T > &other) |
| thistogram< T > & | multiply (const T &cst) |
| thistogram< T > & | multiply (const thistogram< T > &other, const T &cst) |
| thistogram< T > & | operator*= (const T &cst) |
| thistogram< T > & | divide (const T &cst) |
| thistogram< T > & | divide (const thistogram< T > &other, const T &cst) |
| thistogram< T > & | add (const T &cst) |
| thistogram< T > & | operator+= (const T &cst) |
| thistogram< T > & | add (const thistogram< T > &other, const T &cst) |
| thistogram< T > & | normalize (const bool forceUpdateOfNumEntries=false) |
Search for extrema | |
| T | maximum () const |
| ivector | getIndexOfMaximum () const |
| T | minimum () const |
| ivector | getIndexOfMinimum () const |
Serialization interface | |
| virtual bool | write (ioHandler &handler, const bool complete=true) const |
| virtual bool | read (ioHandler &handler, const bool complete=true) |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static const T & | outerBoundsCell () |
Protected Member Functions | |
| int | vectorToIndex (const ivector &x) const |
Protected Attributes | |
| int | totalNumberOfCells |
| T | numberOfEntries |
| int | dimensionality |
| vector< T > | theHistogram |
| ivector | theCellsPerDimension |
| ivector | firstCell |
| ivector | lastCell |
Histogram template class.
The lti::thistogram template class allows the generation of histogram statistics for points in a n-dimensional space.
The elements of the histogram will be indexed in each dimension i between 0 an 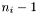 .
.
The class histogram is a typedef of thistogram<double>
The use of this class for the one and two dimensional histograms is not very efficient. You can use the inherited classes lti::histogram1D and lti::histogram2D instead.
The mapping of the analysed m-dimensional space to the n-dimensional index space will be done by mapping functors. The most usual ones are declared as internal types of the class lti::histogram.
Example:
lti::thistogram<float> hist(3,10) // creates a 3D-histogram with 10 // cells pro dimension. The total // number of cells is 10^3=1000
To read the content of a histogram cell use the access operator at(). You can increment the value of a cell with the member put().
| typedef vector<T>::const_iterator lti::thistogram< T >::const_iterator |
The const_iterator is equivalent to a lti::vector<T>::const_iterator.
| typedef vector<T>::iterator lti::thistogram< T >::iterator |
The iterator is equivalent to a lti::vector<T>::iterator.
| lti::thistogram< T >::thistogram | ( | ) |
default constructor creates an empty histogram;
| lti::thistogram< T >::thistogram | ( | const int & | dimensions, | |
| const int & | cells | |||
| ) |
create a histogram of the given dimensionality.
Each dimension will have the given number of cells, i.e. the histogram will have 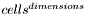 cells.
cells.
| dimensions | the dimensionality of the histogram. | |
| cells | the number of cells per dimension. |
| lti::thistogram< T >::thistogram | ( | const int & | dimensions, | |
| const ivector & | cells | |||
| ) |
create a histogram with the given dimensionality.
Each dimension i will have the number of cells indicated in the i-th element of the vector cells.
If the dimensionaly differs from the size of the given vector, the number of cells of the dimension i will be given by ![$dim_i = cells[i \, mod \, cells.size()]$](form_140.png) .
.
This means, if you want a 6-dimensional histogram, and your cells-vector has only three elements [10,15,5], the number of cells per dimension will be [10,15,5,10,15,5]
| dimensions | the dimensionality of the histogram | |
| cells | a vector with the number of cell per dimension |
| lti::thistogram< T >::thistogram | ( | const thistogram< T > & | other | ) |
create this histogram as a copy of another histogram
| other | the histogram to be copied. |
| virtual lti::thistogram< T >::~thistogram | ( | ) | [virtual] |
destructor
| thistogram<T>& lti::thistogram< T >::add | ( | const thistogram< T > & | other, | |
| const T & | cst | |||
| ) |
Add constant to the other histogram and leave the result here.
Returns a reference to this histogram.
| other | the oder histogram | |
| cst | constant scala to be added with each element of the other histogram |
| thistogram<T>& lti::thistogram< T >::add | ( | const T & | cst | ) |
Add constant to this histogram.
This histogram is changed. Returns this histogram.
| cst | constant scala to be added with each element |
| thistogram<T>& lti::thistogram< T >::add | ( | const thistogram< T > & | first, | |
| const thistogram< T > & | second | |||
| ) |
Add two histogram and leave the result in this object.
| first | the first histogram. The number of entries of both histograms are also added. | |
| second | the second histogram will be added with the first histogram |
| thistogram<T>& lti::thistogram< T >::add | ( | const thistogram< T > & | other | ) |
Add another histogram of the same type and same dimension and leave the result in this object.
The number of entries of both histograms are also added.
| other | the other histogram to be added with |
Referenced by lti::thistogram< float >::operator+=().
| thistogram<T>& lti::thistogram< T >::apply | ( | T(*)(const T &) | function | ) |
applies a C-function to each element of the histogram.
| function | a pointer to a C-function |
| thistogram<T>& lti::thistogram< T >::apply | ( | T(*)(T) | function | ) |
Apply methods.
applies a C-function to each element of the histogram.
| function | a pointer to a C-function |
| T& lti::thistogram< T >::at | ( | const ivector & | x | ) |
access element x of the histogram
| x | index of the histogram element to be accessed. It should be between getFirstCell() and getLastCell() |
| const T& lti::thistogram< T >::at | ( | const ivector & | x | ) | const |
read-only access to the element x of the histogram
| x | index of the histogram element to be accessed. It should be between getFirstCell() and getLastCell() |
| iterator lti::thistogram< T >::begin | ( | ) | [inline] |
returns an iterator pointing to the first element.
The use of the interators is similar to the iterators of the Standard Template Library (STL).
If you need to iterate on all elements of the histogram, you can use following code:
int tmp,accu; // a temporal variable lti::thistogram<float> myHist(3,10); // a 3D-histogram with 10 cells/dim. (of type float) lti::thistogram<float>::iterator it; // an iterator for (it=myHist.begin();it!=myHist.end();it++) { tmp = *it; // tmp has value of element pointed // by the iterator. accu += tmp; (*it) = accu; // change the value in the histogram. }
Please note that if you define it as a const_iterator, you can not make something like *it=accu.
| const_iterator lti::thistogram< T >::begin | ( | ) | const [inline] |
returns an iterator pointing to the first element.
Note that you can not change the values of the histogram elements when you use a const_iterator. See also begin()
Referenced by lti::thistogram< float >::castFrom().
| thistogram<T>& lti::thistogram< T >::castFrom | ( | const thistogram< U > & | other | ) | [inline] |
copy the other histogram by casting each of its elements
| other | The histogram to be casted |
| int lti::thistogram< T >::cellsInDimension | ( | const int & | dimension | ) | const [inline] |
get the number of cells of the dimension dim
| dimension | the index of the dimension to be checked |
dim | const ivector& lti::thistogram< T >::cellsPerDimension | ( | ) | const [inline] |
get the number of cells per dimension
Referenced by lti::thistogram< float >::castFrom().
| void lti::thistogram< T >::clear | ( | ) |
equivalent to resize(0,0);
| virtual mathObject* lti::thistogram< T >::clone | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
create a clone of this histogram
Implements lti::mathObject.
Reimplemented in lti::histogram1D, and lti::histogram2D.
| thistogram<T>& lti::thistogram< T >::copy | ( | const thistogram< T > & | other | ) |
assigment operator.
copy the contents of other in this object.
| other | the source histogram to be copied. |
Reimplemented from lti::ioObject.
Reimplemented in lti::histogram1D, and lti::histogram2D.
Referenced by lti::thistogram< float >::operator=().
| void lti::thistogram< T >::detach | ( | thistogram< T > & | receiver | ) |
Free the data of this object and attach it to the "receiver".
It is a very efficient way to make a copy of this histogram, if you don't need the source data anymore!
At the end of the detachment, this histogram will be empty.
| receiver | the histogram which will receive the memory. this histogram! |
| int lti::thistogram< T >::dimensions | ( | ) | const [inline] |
returns the number of dimensions of this histogram
Referenced by lti::thistogram< float >::castFrom(), and lti::mapperFunctor< Tin, Tout >::parameters::generateFrom().
| thistogram<T>& lti::thistogram< T >::divide | ( | const thistogram< T > & | other, | |
| const T & | cst | |||
| ) |
Divide the other histogram with a constant and leave the result here.
Returns a reference to this histogram.
Keep in mind, that rounding errors might occur if you use this with thistogram<int>.
| other | the histogram to be divide by the constant value | |
| cst | the elements of the histogram will be divided with this constant |
| thistogram<T>& lti::thistogram< T >::divide | ( | const T & | cst | ) |
Divide this histogram with a constant.
Returns this histogram.
Keep in mind, that rounding errors might occur if you use this with thistogram<int>.
| cst | the elements of the histogram will be divided with this constant |
| thistogram<T>& lti::thistogram< T >::emultiply | ( | const thistogram< T > & | first, | |
| const thistogram< T > & | second | |||
| ) |
Elementwise multiplication.
This histogram will contain the elementwise multiplication of the elements in first and second.
Both histograms are first normalized, then multiplied, and the number of entries is after the multiplication 1! After this multiplication, this histogram cannot be anymore interpreted as a histogram, but as a combined probabilty distribution. You can use setNumberOfEntries() to change this fact under your own risk (the semathical meaning of that is left to you!).
You should not use this with thistogram<int>.
| first | the first histogram | |
| second | the second histogram will be multiplied with the first histogram |
| thistogram<T>& lti::thistogram< T >::emultiply | ( | const thistogram< T > & | other | ) |
Elementwise multiplication.
Each element of this histogram will be multiplied with the elements of the other histogram and the result will be left in this object!
Both histograms are first normalized, then multiplied, and the number of entries is after the multiplication 1! After this multiplication, this histogram cannot be anymore interpreted as a histogram, but as a combined probabilty distribution. You can use setNumberOfEntries() to change this fact under your own risk (the semathical meaning of that is left to you!).
You should not use this with thistogram<int>.
The returned histogram is this object!
| other | the other histogram to be multiplied with |
| iterator lti::thistogram< T >::end | ( | ) | [inline] |
returns last index as an iterator For an example see begin()
| const_iterator lti::thistogram< T >::end | ( | ) | const [inline] |
returns last index as a const iterator.
For an example see begin()
Referenced by lti::thistogram< float >::castFrom().
| bool lti::thistogram< T >::equals | ( | const thistogram< T > & | other | ) | const |
compare this histogram with another one.
| other | the other histogram to be compared with |
Referenced by lti::thistogram< float >::operator==().
| void lti::thistogram< T >::fill | ( | const T & | iniValue, | |
| const ivector & | from = ivector(), |
|||
| const ivector & | to = ivector() | |||
| ) |
fills the histogram elements with iniValue between the n-dimensional points from and to.
| iniValue | the elements will be initialized with this value. | |
| from | first element index | |
| to | last element index |
If from or to are out of bounds, they will be (internaly) adjusted to a correct value.
Example:
lti::thistogram<float> hist(1,10); // 1D-histogram with 10 elements hist.clear; hist.fill(9.0f,ivector(1,1),ivector(1,3)); // hist=[0,9,9,9,0,0,0,0,0,0]
| const ivector& lti::thistogram< T >::getFirstCell | ( | ) | const [inline] |
returns a vector to the first element of the histogram (usually every element of the vector is 0;
Reimplemented in lti::histogram1D, and lti::histogram2D.
Referenced by lti::mapperFunctor< Tin, Tout >::parameters::generateFrom().
| ivector lti::thistogram< T >::getIndexOfMaximum | ( | ) | const [inline] |
get the index of the biggest element in the histogram
Reimplemented in lti::histogram1D, and lti::histogram2D.
| ivector lti::thistogram< T >::getIndexOfMinimum | ( | ) | const [inline] |
get the index of the biggest element in the histogram
Reimplemented in lti::histogram1D, and lti::histogram2D.
| const ivector& lti::thistogram< T >::getLastCell | ( | ) | const [inline] |
returns a vector to the last element of the histogram
Reimplemented in lti::histogram1D, and lti::histogram2D.
Referenced by lti::mapperFunctor< Tin, Tout >::parameters::generateFrom().
| const T& lti::thistogram< T >::getNumberOfEntries | ( | ) | const [inline] |
returns the number of entries registered by now.
| double lti::thistogram< T >::getProbability | ( | const ivector & | x | ) | const |
read-only access to the element x of the histogram as a discrete probability distribution term.
This is equivalent to 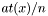 , where n is the number of entries in the histogram (see getNumberOfEntries()).
, where n is the number of entries in the histogram (see getNumberOfEntries()).
| x | index of the histogram element to be accessed. It should be between getFirstCell() and getLastCell() |
x lies outer bounds. | const char* lti::thistogram< T >::getTypeName | ( | void | ) | const [inline, virtual] |
returns the name of this class: "histogram"
Reimplemented from lti::mathObject.
Reimplemented in lti::histogram1D, and lti::histogram2D.
| void lti::thistogram< T >::initialize | ( | const T & | value = T(0) |
) |
initialize all cells of the histogram with 0 (or another specified number).
Reimplemented in lti::histogram1D, and lti::histogram2D.
| T lti::thistogram< T >::maximum | ( | ) | const [inline] |
search for the maximum entry in the histogram and return its value
| T lti::thistogram< T >::minimum | ( | ) | const [inline] |
search for the minimum entry in the histogram and return its value
| thistogram<T>& lti::thistogram< T >::multiply | ( | const thistogram< T > & | other, | |
| const T & | cst | |||
| ) |
Multiply the other histogram with a constant and leave the result here.
Returns a reference to this histogram. Note that if you use this operation, the number of entries could be false at the end due to numerical instabilities.
| other | the other histogram to be multiplied with the constant value | |
| cst | constant scalar to be multiplied with the other histogram. |
| thistogram<T>& lti::thistogram< T >::multiply | ( | const T & | cst | ) |
Multiply this histogram with a constant.
Returns this histogram. The total number of entries will also be updated. Note that if you use this operation, the number of entries could be false at the end due to numerical instabilities.
| cst | constant scalar to be multiplied with |
Referenced by lti::thistogram< float >::operator*=().
| thistogram<T>& lti::thistogram< T >::normalize | ( | const bool | forceUpdateOfNumEntries = false |
) |
Normalize the histogram.
The default behaviour just divides the content of each bin by the current number of entries. Since some operations (especially if you use apply()) can "corrupt" the consistence of this internal attribute, you can additionally specify with the boolean parameter, that you want to force the recomputation the number of entries.
The total number of entries will be set to 1.0 You should not use this with thistogram<int>.
| forceUpdateOfNumEntries | if true, the number of entries will be recomputed, ignoring their previous content. If false (default), the current value will be used. |
| thistogram<T>& lti::thistogram< T >::operator*= | ( | const T & | cst | ) | [inline] |
alias for multiply(const T& cst)
| cst | constant scalar to be multiplied with |
| thistogram<T>& lti::thistogram< T >::operator+= | ( | const T & | cst | ) | [inline] |
Alias for add(const T& cst).
| thistogram<T>& lti::thistogram< T >::operator+= | ( | const thistogram< T > & | other | ) | [inline] |
Alias for add(const histogram& other).
| thistogram<T>& lti::thistogram< T >::operator-= | ( | const thistogram< T > & | other | ) | [inline] |
Alias for substract(const histogram& other).
| thistogram<T>& lti::thistogram< T >::operator= | ( | const thistogram< T > & | other | ) | [inline] |
assigment operator (alias for copy(other)).
| other | the histogram to be copied |
Reimplemented from lti::ioObject.
Reimplemented in lti::histogram1D, and lti::histogram2D.
| bool lti::thistogram< T >::operator== | ( | const thistogram< T > & | other | ) | const [inline] |
compare this histogram with other
| other | the other histogram to be compared with |
| static const T& lti::thistogram< T >::outerBoundsCell | ( | ) | [inline, static] |
Variable with a negative value to indicate outer bounds access!
| bool lti::thistogram< T >::prettyCloseTo | ( | const thistogram< T > & | other, | |
| const T & | tolerance | |||
| ) | const |
compare this histogram with another one, and use the given tolerance to determine if the value of each element of the other histogram approximately equals the values of the actual histogram elements.
An element x is approximately equal to another element y with a tolerance t, if following equation holds: x-t < y < x+t
| other | the other histogram to be compared with | |
| tolerance | the tolerance to be used |
| const T& lti::thistogram< T >::put | ( | const ivector & | x, | |
| const T & | increment = T(1) | |||
| ) |
increment the cell at x by the given number of elements (or 1.0 if nothing is explicitly indicated!) and update the number of entries in the histogram.
| x | index of the histogram element to be incremented | |
| increment | amount of the incrementation (default: 1) |
| virtual bool lti::thistogram< T >::read | ( | ioHandler & | handler, | |
| const bool | complete = true | |||
| ) | [virtual] |
read the object from the given ioHandler
Reimplemented from lti::mathObject.
Reimplemented in lti::histogram1D, and lti::histogram2D.
Referenced by lti::read().
| void lti::thistogram< T >::resize | ( | const int & | dimensions, | |
| const ivector & | cells | |||
| ) |
change dimensionality and cell number of the histogram.
All data will be lost!
| dimensions | the new dimensionality of the histogram | |
| cells | the number of cells per dimension |
| void lti::thistogram< T >::resize | ( | const int & | dimensions, | |
| const int & | cells | |||
| ) |
change dimensionality and cell number of the histogram.
All data will be lost!
| dimensions | the new dimensionality of the histogram | |
| cells | the number of cells per dimension |
Reimplemented in lti::histogram2D.
Referenced by lti::thistogram< float >::castFrom().
| void lti::thistogram< T >::setNumberOfEntries | ( | const T & | newNumberOfEntries | ) |
Normalize the histogram and then denormalize it with the given number of entries.
You should not use this for thistogram<int>, since rounding errors are likely to occur.
| thistogram<T>& lti::thistogram< T >::subtract | ( | const thistogram< T > & | first, | |
| const thistogram< T > & | second | |||
| ) |
Subtracts two histograms and leaves the result in this object.
| first | the first histogram | |
| second | the second histogram will be substracted from the first histogram |
| thistogram<T>& lti::thistogram< T >::subtract | ( | const thistogram< T > & | other | ) |
Subtracts another histogram of the same type and same dimension and leaves the result in this object.
| other | will be substracted from this histogram |
Referenced by lti::thistogram< float >::operator-=().
| void lti::thistogram< T >::updateNumberOfEntries | ( | ) |
counts the number of entries in the whole histogram and sets the internal counter for the total number of entries.
if some direct access to the cell contents have been done, you should update the number of entries with this function
Referenced by lti::thistogram< float >::castFrom().
| int lti::thistogram< T >::vectorToIndex | ( | const ivector & | x | ) | const [inline, protected] |
| virtual bool lti::thistogram< T >::write | ( | ioHandler & | handler, | |
| const bool | complete = true | |||
| ) | const [virtual] |
write the object in the given ioHandler
Reimplemented from lti::mathObject.
Reimplemented in lti::histogram1D, and lti::histogram2D.
Referenced by lti::write().
int lti::thistogram< T >::dimensionality [protected] |
the dimensionality of this histogram
ivector lti::thistogram< T >::firstCell [protected] |
a vector with the right dimension initialized with 0
Reimplemented in lti::histogram1D, and lti::histogram2D.
ivector lti::thistogram< T >::lastCell [protected] |
a vector with the right dimension initialized with the number of cells - 1 per dimension
Reimplemented in lti::histogram1D, and lti::histogram2D.
T lti::thistogram< T >::numberOfEntries [protected] |
the registered number of entries
ivector lti::thistogram< T >::theCellsPerDimension [protected] |
number of cells
vector<T> lti::thistogram< T >::theHistogram [protected] |
the data of the histogram
Referenced by lti::thistogram< float >::begin(), lti::thistogram< float >::end(), lti::thistogram< float >::maximum(), and lti::thistogram< float >::minimum().
int lti::thistogram< T >::totalNumberOfCells [protected] |
the total number of cells