

|
latest version v1.9 - last update 10 Apr 2010 |
|
Split image in its L u
u v
v channels.
More...
channels.
More...
#include <ltiSplitImageToCIELuv.h>
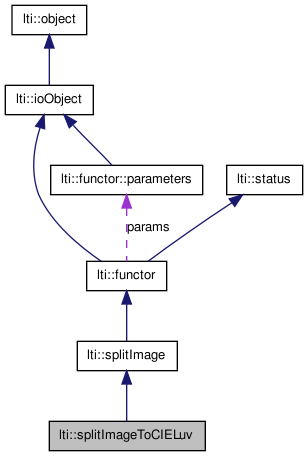
Public Member Functions | |
| splitImageToCIELuv () | |
| virtual const char * | getTypename () const |
| virtual functor * | clone () const |
| virtual bool | apply (const image &img, channel &c1, channel &c2, channel &c3) const |
| virtual bool | apply (const rgbPixel &pixel, float &c1, float &c2, float &c3) const |
Protected Member Functions | |
| virtual bool | apply (const image &img, channel8 &c1, channel8 &c2, channel8 &c3) const |
| virtual bool | apply (const rgbPixel &pixel, ubyte &c1, ubyte &c2, ubyte &c3) const |
Static Protected Attributes | |
| static const float * | lut |
| static const int | lutSize |
Split image in its L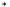 u
u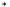 v
v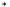 channels.
channels.
The following is an excerpt of this page
CIE 1976 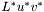 (CIELUV) is based directly on CIE XYZ and is another attempt to linearize the perceptibility of color differences. The non-linear relations for
(CIELUV) is based directly on CIE XYZ and is another attempt to linearize the perceptibility of color differences. The non-linear relations for 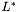 ,
, 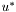 , and
, and 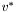 are given below:
are given below:
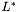 = 116 * (Y/Yn)1/3 - 16
= 116 * (Y/Yn)1/3 - 16
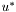 = 13L* * ( u' - un' )
= 13L* * ( u' - un' )
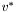 = 13L* * ( v' - vn' )
= 13L* * ( v' - vn' )
The quantities un' and vn' refer to the reference white of the light source; for the 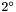 observer and illuminant C, un' = 0.2009, vn' = 0.4610 [ 1 ]. Equations for u' and v' are given below:
observer and illuminant C, un' = 0.2009, vn' = 0.4610 [ 1 ]. Equations for u' and v' are given below:
u' = 4X / (X + 15Y + 3Z) = 4x / ( -2x + 12y + 3 )
v' = 9Y / (X + 15Y + 3Z) = 9y / ( -2x + 12y + 3 )
The transformation from (u',v') to (x,y) is:
x = 27u' / ( 18u' - 48v' + 36 )
y = 12v' / ( 18u' - 48v' + 36 )
The transformation from CIELUV to XYZ is performed as following:
u' = u / ( 13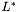 ) + un
) + un
v' = v / ( 13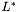 ) + vn
) + vn
Y = (( 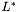 + 16 ) / 116 )3
+ 16 ) / 116 )3
X = - 9Yu' / (( u' - 4 ) v' - u'v' )
Z = ( 9Y - 15v'Y - v'X ) / 3v'
The 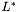 value with these definitions will be between 0 and 100. This functor ensure that the outputs will be put into the usual values in the LTI-Lib, i.e. for channels the outputs will be normalized by 100, so that the luminance channel will be between 0 and 1.0. The u channel will get values between -0.865731 to 1.72906 and the v channel from -1.30445 to 1.16047.
value with these definitions will be between 0 and 100. This functor ensure that the outputs will be put into the usual values in the LTI-Lib, i.e. for channels the outputs will be normalized by 100, so that the luminance channel will be between 0 and 1.0. The u channel will get values between -0.865731 to 1.72906 and the v channel from -1.30445 to 1.16047.
For channel8 outputs this color space doesn't make much sense, since some values are negative.
| lti::splitImageToCIELuv::splitImageToCIELuv | ( | ) |
default constructor.
Initializes (only once) the lut for the cubic root, with 2048 entries.
| virtual bool lti::splitImageToCIELuv::apply | ( | const rgbPixel & | pixel, | |
| ubyte & | c1, | |||
| ubyte & | c2, | |||
| ubyte & | c3 | |||
| ) | const [protected, virtual] |
on-copy Do not use this method yet! The output values will contain invalid data due to underflows and overflows of the valid value range!
Implements lti::splitImage.
| virtual bool lti::splitImageToCIELuv::apply | ( | const image & | img, | |
| channel8 & | c1, | |||
| channel8 & | c2, | |||
| channel8 & | c3 | |||
| ) | const [protected, virtual] |
on-copy Do not use this method yet! The output channels will contain invalid data due to underflows and overflows of the channel valid value range!
Implements lti::splitImage.
| virtual bool lti::splitImageToCIELuv::apply | ( | const rgbPixel & | pixel, | |
| float & | c1, | |||
| float & | c2, | |||
| float & | c3 | |||
| ) | const [virtual] |
on-copy Note that the output values will contain values outside the interval 0.0-1.0.
Implements lti::splitImage.
| virtual bool lti::splitImageToCIELuv::apply | ( | const image & | img, | |
| channel & | c1, | |||
| channel & | c2, | |||
| channel & | c3 | |||
| ) | const [virtual] |
on-copy Note that the output channels will contain values outside the interval 0.0-1.0.
Implements lti::splitImage.
| virtual functor* lti::splitImageToCIELuv::clone | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
returns a pointer to a clone of the functor
Implements lti::functor.
| virtual const char* lti::splitImageToCIELuv::getTypename | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
returns the name of this type
const float* lti::splitImageToCIELuv::lut [static, protected] |
look-up-table for cubic root
const int lti::splitImageToCIELuv::lutSize [static, protected] |
size of the lut for cubic root